Blog
1. Hazardous area (hazardous area components)
2. Hazardous industrial facilities (examples of hazardous industrial facilities)
3. Types of explosion protection (intrinsically safe and explosion proof enclosure)
1. Pressure Gauge application
2. Pressure gauge types and its operating principle (mechanical and digital pressure gauges)
3. The pros and cons of mechanical and digital pressure gauges
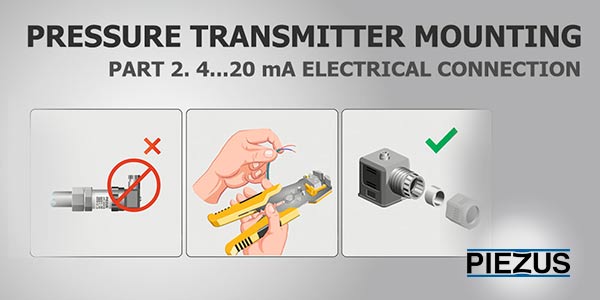
Pressure transmitter mounting. Part 2. 4-20 mA electrical connection
1. Connecting cable to DIN 43650
2. Mounting DIN 43650 connector
3. Signal cable position rules
4. Electrical couplings connection rules
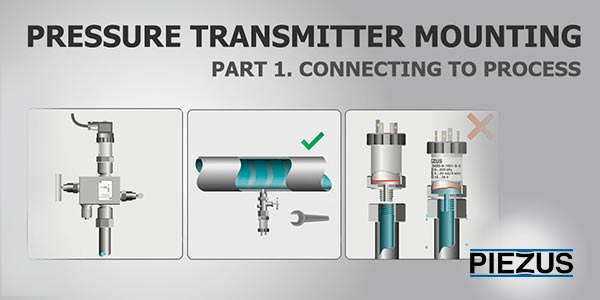
Pressure transmitter mounting. Part 1. Connecting to process
1. Using valves and valve blocks
2. Connecting transmitter to process
3. Pressure port seal
4. Mounting pressure into enclosed volume
5. Using pressure snubber
1. The Physical Quantity Pressure
2. Pressure units
3. Gas pressure
4. Hydrostatic Pressure of a Liquid
5. Atmospheric Pressure
6. Absolute, Gauge and Differential Pressure
7. Instrument for Pressure Measurement
1. Pressure Switch operating principle (common pressure switch application)
2. Pressure Switch types (electronic and mechanical pressure switch)
3. The pros and cons of mechanical and electronic pressure switches
Submersible Pressure Transmitter Installation
- Selection of installation location
- Submersible Pressure Transmitter Mounting (the use of special clamps: cable clamp with rubber sealing sleeve or cable hanger)
- Connecting submersible pressure transmitter to termination box (termination box installation; the use of hydrometric cable and regular cable)
1. Hydrostatic liquid level measurement method.
2. Hydrostatic pressure transmitters.
3. Submersible pressure transmitter.
4. Submersible pressure transmitter's application.
1. Connecting cable to DIN 43650.
2. Mounting DIN 43650.
3. Signal cable positioning rules.
4. Electrical couplings connection rules.
1. Using valves and valve blocks.
2. Connecting transmitter to process.
3. Pressure port seal.
4. Mounting pressure transmitter into enclosed volume.
5. Using pressure snubber.
1. Pressure: the physics.
2. Types of pressure (absolute, gauge, differential).
3. Types of pressure transmitters (set-in/submersible).
4. Design of pressure transmitters (mechanical connection (ports), sensor, electronic module, electrical connection).
5. Pressure transmitters: areas of application.
What is the difference between the nonlinearity calculated by TPM method and BFSL method?
The basic accuracy specified by manufacturers of pressure and level transmitters in their datasheets includes nonlinearity, hysteresis and repeatability. Very often, next to nonlinearity data you see "BFSL" and / or "TPM". These are two different approaches to calculating nonlinearity...